- If there is one thing you should remember from this guide, it should be these five things:
- Self-directed IRAs, self-directed 401(k)s, or other self-directed accounts allow you to invest in alternative assets and give you greater control than traditionally seen assets.
- Assets such as real estate, private equity, precious metals, and more can provide diversification and potentially higher returns, but they also bring other risk factors.
- Do proper due diligence and familiarize yourself with the liquidity, valuation, and rules before investing in each asset.
- If you want to explore alternative investments, it’s best to speak with a professional who is knowledgeable about them to help you avoid complexity and ensure compliance.
- Alternative investment options can offer higher growth, but may require additional administrative work and are more prone to being subject to prohibited transactions than traditional investment options.
Traditional vs. Self-Directed Asset Access
| Feature | Traditionally seen IRA or 401(k) | Self-Directed IRA or 401(k) | Key Difference |
| Available Assets | Stocks, Bonds, Mutual Funds, ETFs | Real Estate, Private Equity, Precious Metals, Cryptos | Broader investment universe |
| Investment Control | Limited options by the plan administrator | Full control over asset selection | Investor empowerment |
| Setup Complexity | Automatic enrollment, possibly employer-managed | Requires a specialized custodian/administrator | Higher initial setup effort |
| Regulatory Oversight | ERISA, IRS rules on standard assets | ERISA, IRS rules, prohibited transactions | More emphasis on transaction compliance |
Risk-Return Profile of Common Alternative Assets
| Asset Type | Typical Return Potential* | Liquidity Profile | Risk Profile |
| Real Estate (Direct) | Moderate to High | Low (Long selling cycles) | Moderate (Market cycles, management) |
| Private Equity/Funds | High | Very Low (Long lock-up periods) | High (Illiquidity, business failure) |
| Precious Metals (Physical) | Low to Moderate | Moderate (Market dependent) | Low (Inflation hedge, price volatility) |
| Cryptocurrencies | Very High (Volatile) | High (24/7 exchanges) | Very High (Extreme volatility, regulation) |
*These return estimates are generalized assumptions and are not guaranteed for every type of investment. Each investment must undergo proper due diligence by the fiduciary of the retirement account before proceeding.
Launch Checklist
- Schedule a call with a new account specialist to find out which self-directed accounts you qualify for.
- Open up a self-directed account at an institution that specializes in self-directed accounts.
- Make contributions, transfer existing IRA accounts, or roll over old employer 401(k)s into your self-directed account.
- Conduct rigorous due diligence on select alternative asset opportunities.
Follow‑Up Checklist
- Assess asset performance against retirement goals regularly.
- Rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain the desired asset allocation.
- Keep abreast of tax and regulatory adjustments, which impact your assets.
- Track liquidity and arrange exit plans if necessary.
Introduction
For decades, the standard advice for retirement savings has been a steady diet of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds within an IRA or 401(k). But what if you’re looking for something more? What if you’ve seen the market’s ups and downs and wondered if there was another path to growth and true diversification? There is an old saying, “Don’t put all your eggs in Wall Street’s basket.” The idea of spreading risk beyond publicly-traded securities isn’t new, but accessing alternative assets within a tax-advantaged account has become more feasible for savvy investors. This isn’t about chasing speculative fads; it’s about strategic diversification. We’re talking about assets that historically have low correlation with traditional markets, like real estate, private equity, or even precious metals. Imagine the potential for steady income from a rental property, or participating in the growth of a promising private company, all within your retirement vehicle. However, it’s not a set-it-and-forget-it strategy. Investing in alternatives inside an IRA or 401(k) requires careful planning, a deep understanding of complex rules, and often a higher degree of administrative management. But for those willing to do their homework, it can open up a world of new possibilities for long-term wealth creation. Let’s explore how you can broaden your retirement horizons.
Table of Contents
Section 1: Learning About Alternative Investments in Your IRA or 401(k)
- What are alternative assets in an IRA or 401(k)?
- Why should I look to alternative assets for my retirement portfolio?
- What retirement plans allow for alternative investments?
- Are there any restrictions on income or employment to use alternative assets with an IRA or 401(k)?
Section 2: Alternative Assets and Their Characteristics
- Is real estate investing with my IRA or 401(k) possible?
- What about private equity or venture capital funds?
- Can I store precious metals such as gold or silver in my IRA or 401(k)?
- How to invest in cryptocurrency in an IRA or 401(k)?
Section 3: Establishing and Funding Your Self-Directed Account
- What is a self-directed retirement account, and how does it pave the way for alternative investments?
- How do I locate a custodian/ administrator for a self-directed IRA or 401(k)?
- Can I convert an existing 401(k) or IRA to a self-directed account?
- What are the average expenses of a self-directed IRA or 401(k) and other assets?
Section 4: Risks, Rewards, and Compliance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Section 1: Alternative Assets in Your 401(k)
FAQ 1: What are alternative assets in an IRA or 401(k)?
Alternative assets are investments other than stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or ETFs inside a retirement account. They are typically accessed through an account administered by a third-party administrator or custodian who specializes in the private market. These can include real estate, private equity, precious metals, cryptocurrencies, and more. They vary in risk, return, and liquidity. When dealing with alternative assets inside a self-directed retirement account, it’s important to understand the prohibited transaction rules.
FAQ 2: Why should I have alternative assets in my retirement portfolio?
Alternative assets increase diversification and decrease overall risk. They can offer a hedge against inflation, additional income, or growth that is not correlated with the stock market. Many people prefer to be able to control more of their savings and not be completely at the mercy of the peaks and valleys of the market. This is suitable for those with an interest in or expertise in options such as real estate.
FAQ 3: What types of retirement plans can be invested in alternatives?
Most IRA plans, including personal plans such as Traditional and Roth IRAs, as well as self-employed plans like SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs, and Solo 401(k)s, and even Health Savings Accounts, can invest in alternative assets. Unlike a traditionally thought of employer-sponsored plan, you have more control to choose the assets your retirement account invests in with a self-directed account. It requires a custodian or third-party administrator with experience in alternative assets to see which accounts they have available that you qualify for.
FAQ 4: Are there any restrictions on income to use alternative assets with an IRA or 401(k)?
Yes, depending on the account. For plans like Traditional IRAs, SEP IRAs, or Solo 401(k)s, there is no income limitation to contribute to the account to invest in alternative assets. There are income phase-out limits to contributing directly to a Roth IRA; however, investors utilize another strategy to still have and grow a Roth IRA account, called a backdoor Roth, which involves converting pre-tax money, like a contribution, to a Roth IRA, since conversions don’t have a limitation.
Section 2: Alternative Assets, Types, & Characteristics
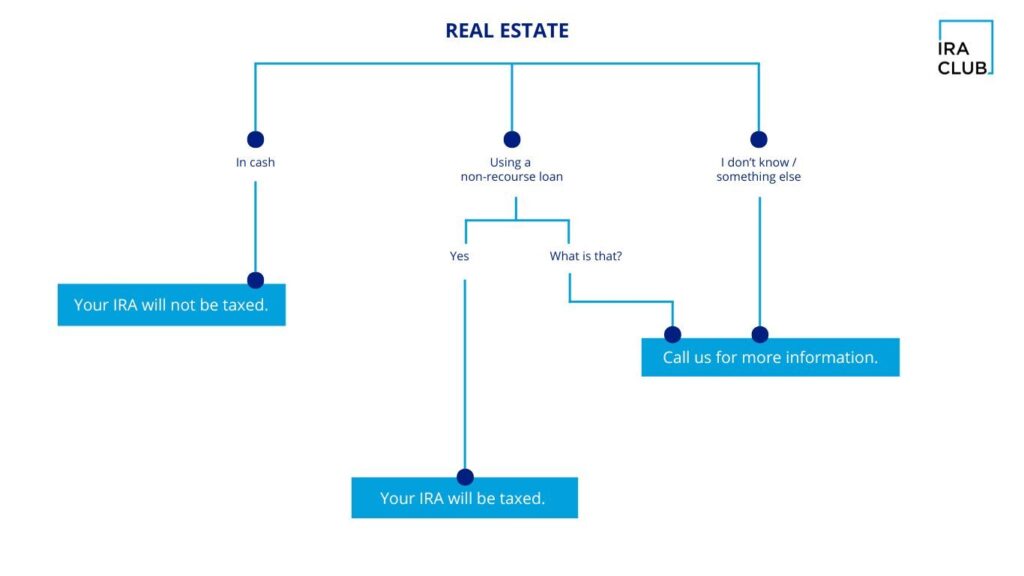
FAQ 5: Can I invest in real estate within my IRA or 401 (k)?
Yes, via a self-directed retirement account. You can have your IRA invest in alternative assets such as real estate, private equity, precious metals, and more. The investment is not yours, but rather the plan’s. You need to abide by IRS rules and stay away from prohibited transactions.
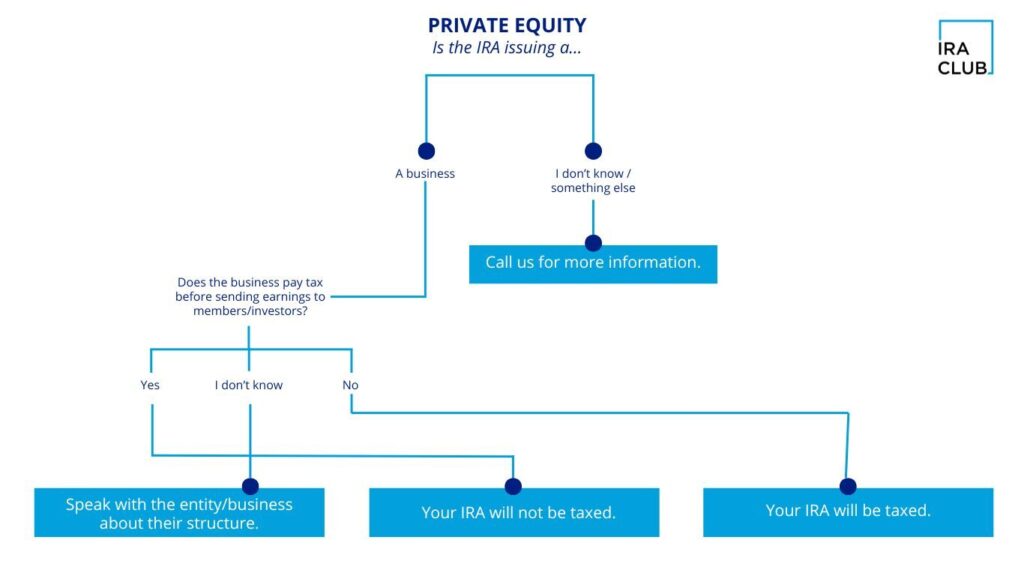
FAQ 6: Private equity or venture capital funds?
You can invest in private equity or VC funds in a self-directed retirement account, as long as it’s completely passive. These are often capital-intensive, have long lock-up periods, and are difficult to sell. This is because of the high risk and the possibility of a higher return, as well as the possibility of losing everything. Do your homework and research the fund manager and companies.
FAQ 7: Can I own precious metals such as gold or silver in my IRA or 401(k)?
Yes. A self-directed retirement account is allowed to hold IRS-approved precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, or palladium on behalf of the plan. The metals must be kept in an approved trustee or depository and not in your home. Stocks can help offset inflation but pay no income. Bars and coins have to be of a certain fineness.
FAQ 8: What are the investment regulations for cryptocurrencies in an IRA or 401(k)?
Crypto can be held in a self-directed retirement account. This approach carries regulatory risk and very stringent IRS rules on valuation and prohibited transactions. Crypto is highly volatile, as well as new, so it is a high-risk strategy.
Section 3: Establishing and Financing Your Self-Directed Retirement Account
FAQ 9: What is a self-directed retirement account, and how does it enable alternative investments?
A self-directed retirement account is a retirement account that can access alternative investment options outside of the stock market. A self-directed retirement account can be an IRA, a 401(k), or even a Health Savings Account, and creates an avenue for investors to strengthen their portfolio diversity with hard assets like real estate. These types of accounts are held at custodians or third-party administrators that specialize in self-directed accounts.
FAQ 10: How can I identify a custodian or administrator for a self-directed retirement account?
Choosing a firm is a personal choice and requires research into characteristics that are most important to you. If you’re interested in alternative assets, strong IRA and investment expertise, and white-glove concierge customer serivce, consider administrators such as the IRA Club. Choose firms with experience in alternatives, good compliance records, and transparent fees. Conduct online research, seek advice from advisors, and join forums to identify trustworthy providers. Ensure that they support your alternative assets of choice and understand valuation reporting.
Talk to an IRA Club Expert Now
FAQ 11: Can I convert an existing 401(k) or IRA to a self-directed retirement account?
Yes, if you no longer work for that company, you can roll over your 401(k) funds into a self-directed IRA without penalty. Discuss the rules with the new custodian and the existing plan.
FAQ 12: What are the average fees related to a self-directed retirement account and alternative assets?
Fee structure can vary from institution to institution. At IRA Club, we have a flat fee model, starting at a $195 annual membership and $195 per holding annually.
Section 4: Risk, Reward, and Compliance
FAQ 13: What are the major risks of alternative assets in a self-directed retirement account?
The major risks include lack of liquidity (which means they typically cannot be sold at short notice) and difficult valuations (private assets do not have daily prices like shares). There is also an increased complexity that comes with alternatives, fraud risk, and an understanding of the prohibited transactions rules to avoid serious violations that can terminate the plan. This is why it’s important to understand if a self-directed account is right for you, and you have a compliant and knowledgeable administrator administering your accounts.
FAQ 14: What IRS rules/prohibited transactions should I be aware of?
Bottom line, the IRS does not allow you to use your retirement accounts to benefit you or lineal family members directly until you decide to take out money at retirement age as a distribution. Examples include purchasing real estate from oneself, hiring a prohibited party’s company to provide a service, or personally managing an asset. Prohibited transaction rules are more complex than this, and a consultation with an IRA expert is recommended before engaging in any transaction that could result in a prohibited transaction. Failure to comply with these rules may result in taxes, penalties, or plan disqualification.